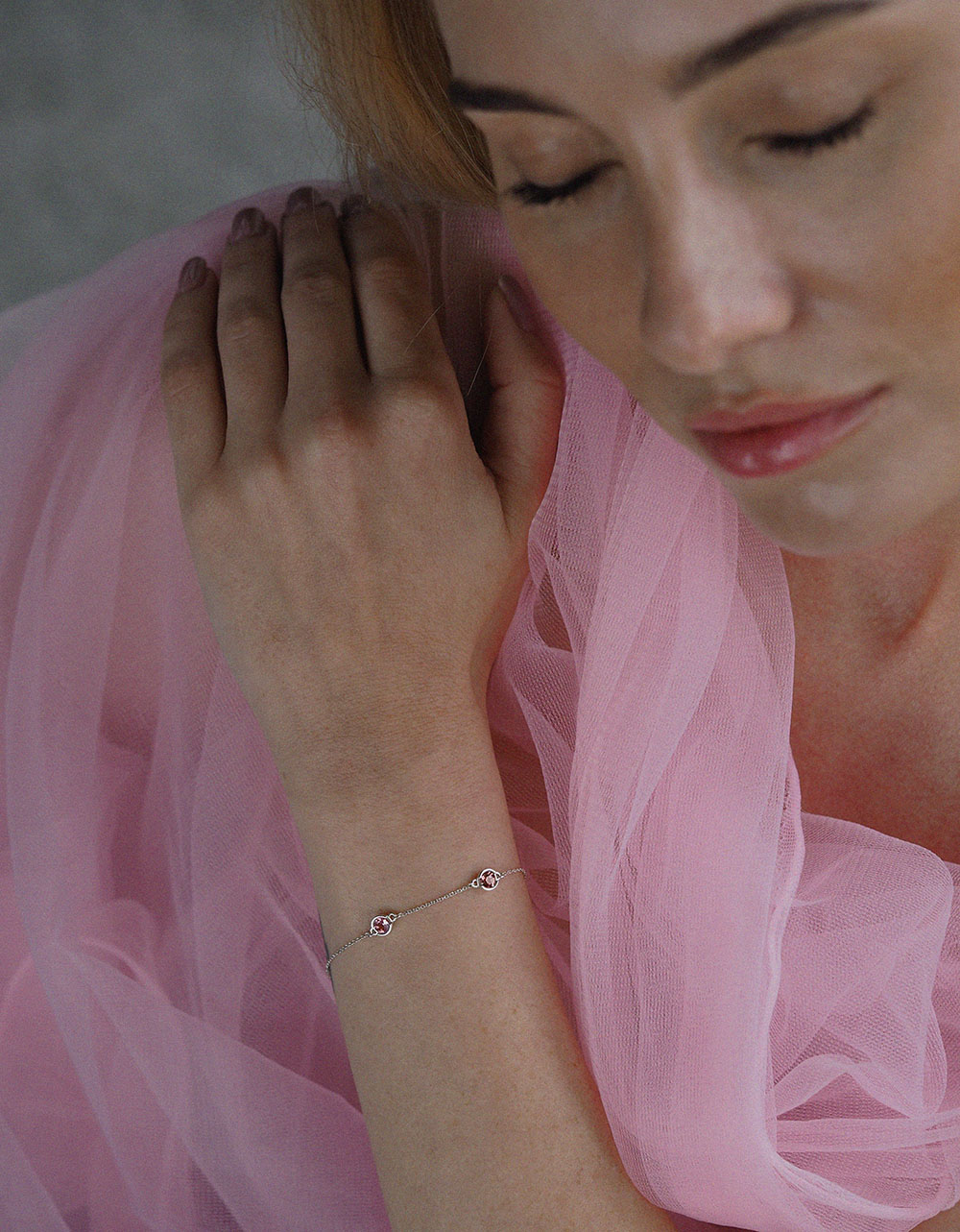
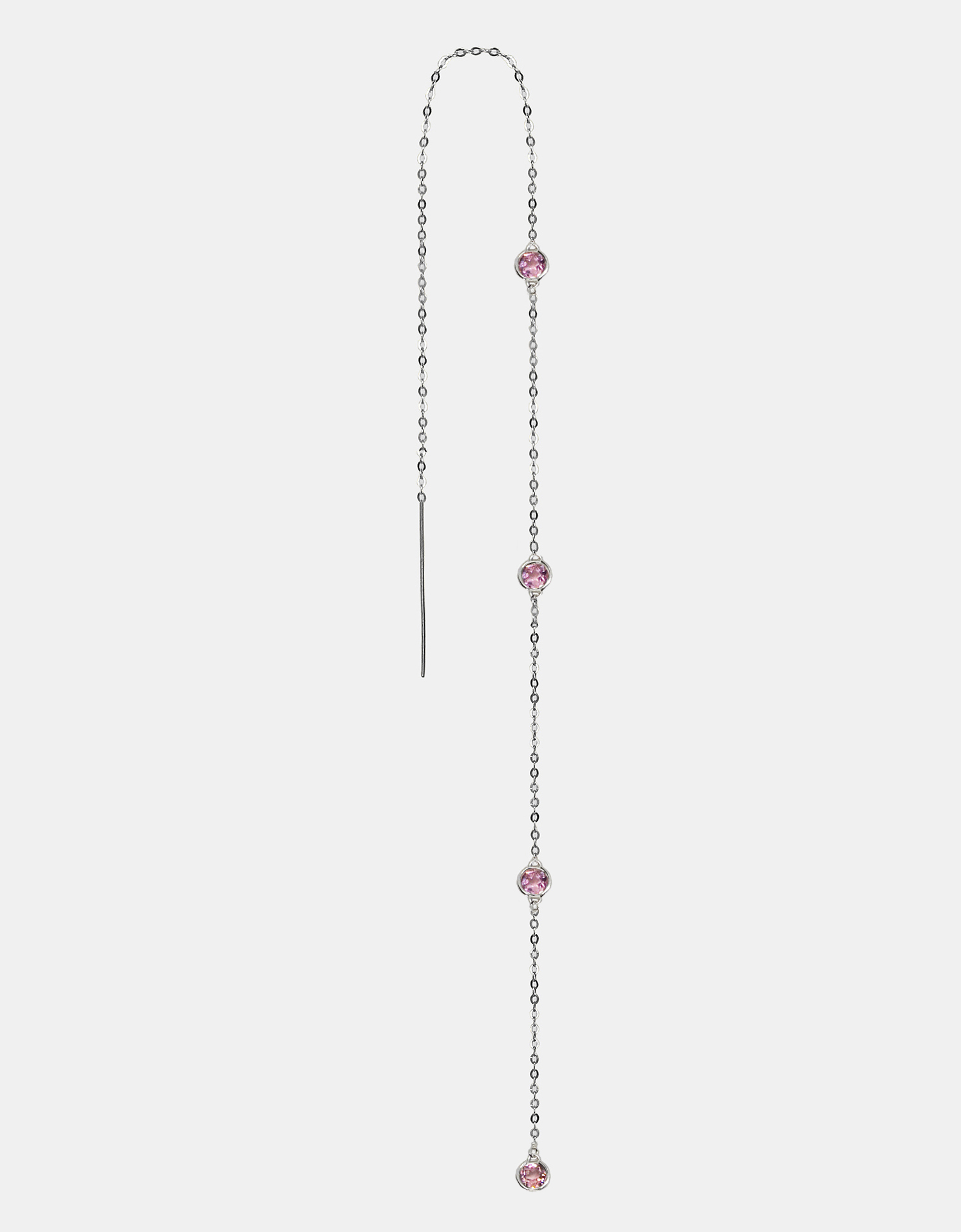
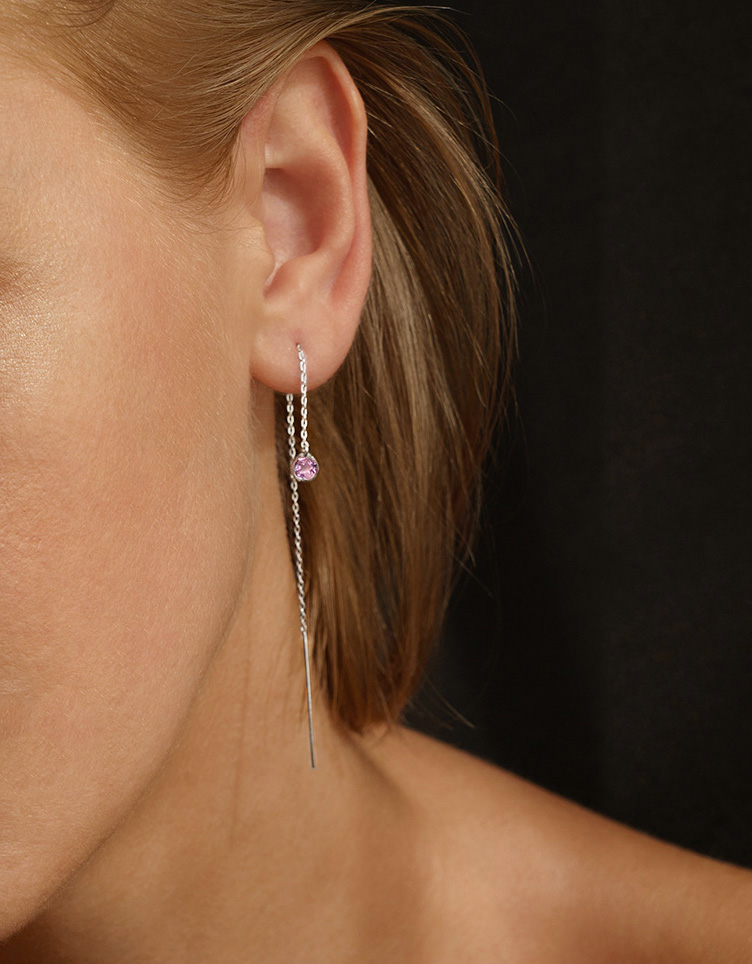- Silver
- Gold
-
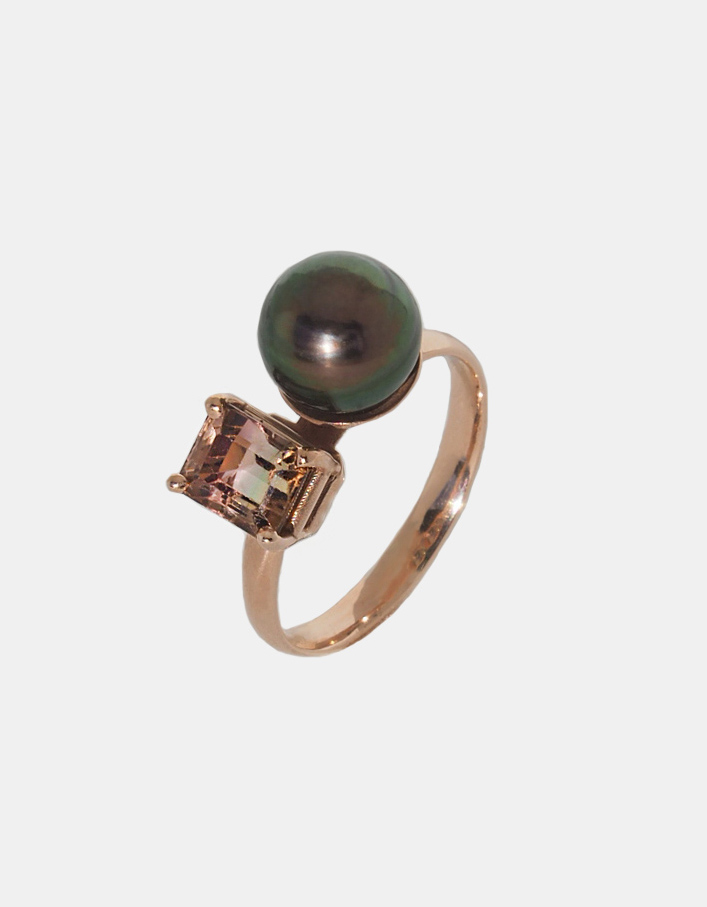
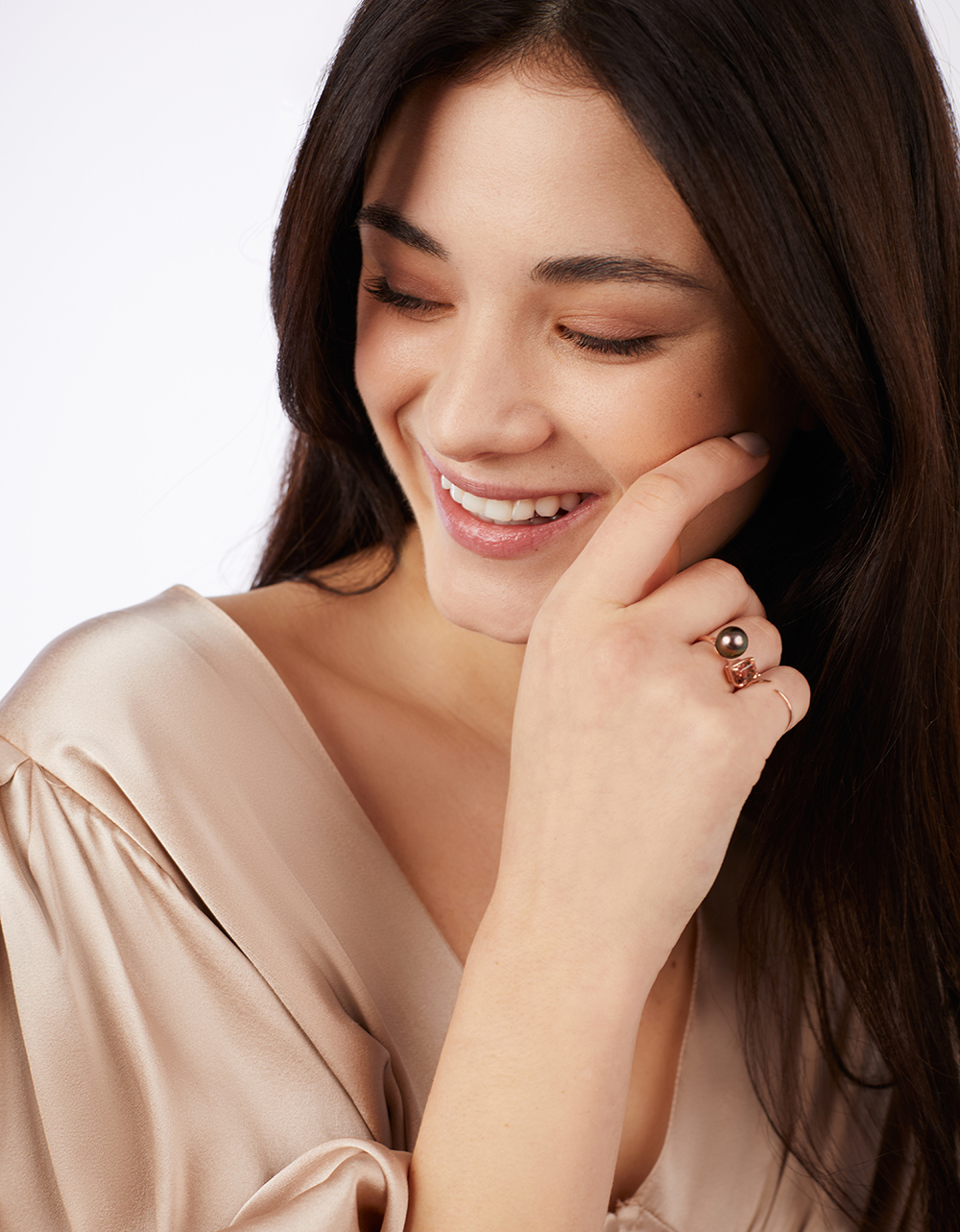
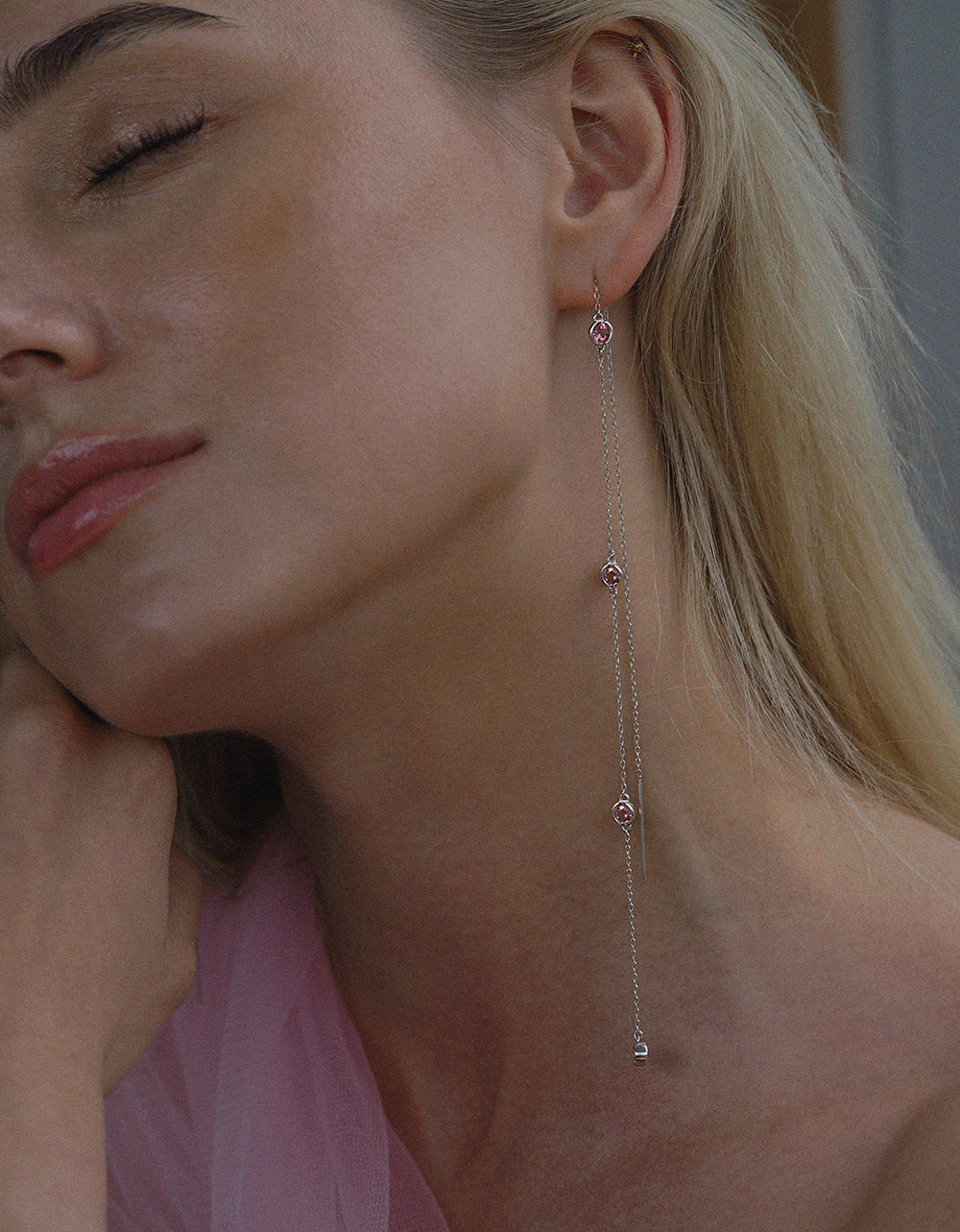
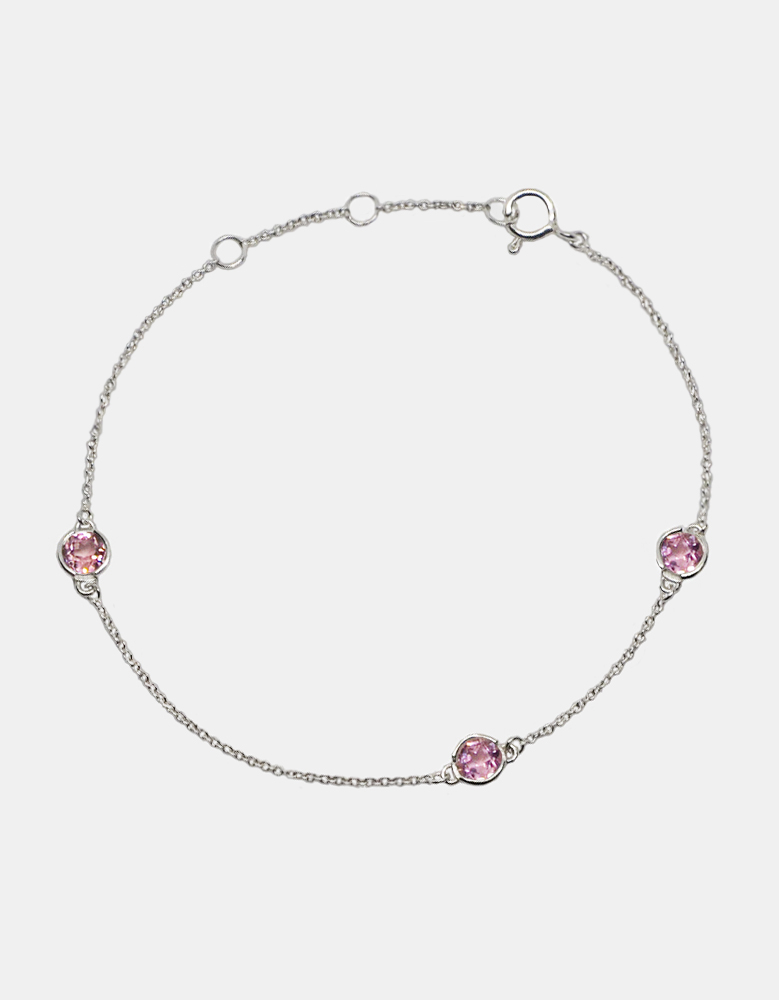
Natural Gemstones
Natural Gemstones
-
Diamonds
Diamonds
-
Wedding and Engagement
Wedding and Engagement
- Baby Born
- Men's
-
Collections
Collections
- Gifts
- Boutiques